The Debt Dynamics of Oil Majors in 2025: ConocoPhillips, EOG, and Marathon Petroleum Under the Lens
A strategic breakdown of capital structure, senior notes, maturity ladders, and credit ratings across three U.S. oil leaders.
Introduction
As 2025 unfolds, the capital structures of major oil and gas companies are shifting in response to rising capital costs, macroeconomic volatility, and divergent corporate strategies. For investors, leverage trends aren’t just a credit signal—they’re a window into operational confidence, capital discipline, and risk tolerance.
In this report, we examine the debt positioning of three U.S. energy players: ConocoPhillips (COP), EOG Resources (EOG), and Marathon Petroleum (MPC). Each offers a distinct playbook—EOG’s fortress balance sheet, COP’s post-acquisition recalibration, and MPC’s debt-heavy refinancings.
📈 Follow PetroSymposium for data-driven coverage of energy capital flows, balance sheet health, and credit-market risk.
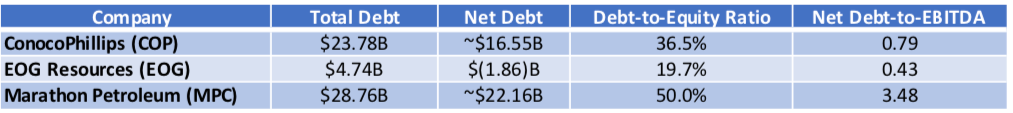
Q1 2025 Financial Data
Key Takeaways
ConocoPhillips (COP): Moderate leverage, active liability management post-M&A.
EOG Resources (EOG): Negative net debt, outsized liquidity, and discipline in debt uptake.
Marathon Petroleum (MPC): Highest leverage among peers; depends on rate-sensitive refinancings.
Senior Note Issuances: A Closer Look
ConocoPhillips (Dec 2024)
Issued $5B in senior notes (5 tranches, maturing 2030–2065) at 4.70%–5.65%.
Purpose: Optimize capital structure and fund long-cycle flexibility.
Investor takeaway: Extending maturity profile limits near-term rollover risk post-Marathon Oil acquisition.
EOG Resources (Nov 2024)
Issued $1B in 30-year notes at 5.65%.
Used to repay $500M in 3.15% notes due 2025 and fund CapEx.
Investor takeaway: Debt raise remains surgical. EOG avoids bloated debt loads even while investing heavily.
Marathon Petroleum (Feb 2025)
Issued $2B total:
$1.1B @ 5.15% (2030)
$900M @ 5.70% (2035)
Replaced $1.25B in 4.70% notes maturing in May 2025.
Investor takeaway: Refinancing keeps operations funded, but rising coupon costs will weigh on cash interest burden if repeated.
Debt Tender Activity: Early Moves to Reduce Risk
ConocoPhillips (Dec 2024):
Launched two tender offers:
“Any and All Notes”: $2.67B
“Maximum Offer Notes”: $2.28B
Objective: Reshape debt stack, lower near-term obligations.
Strategic angle: Shows proactive financial engineering as leverage ticks up from Marathon Oil deal.
Debt Maturity Profiles & Liquidity Positions
Liquidity Overview
ConocoPhillips:
Total debt rose to $24.3B at end-2024, driven by $5.2B in new debt and $4.6B assumed from the Marathon Oil acquisition. Offset by $4.1B in repurchases and extended maturities to reduce short-term pressure.EOG Resources:
Carried $3.78B in debt vs. $6.12B in cash (as of Sept 2024). Plans to increase debt modestly to $5–6B by late 2026, while keeping net debt/EBITDA under 1.0x. Strong free cash flow continues to support both reinvestment and shareholder returns.Marathon Petroleum:
Issued $2B in early 2025 to cover 2025 maturities and maintain liquidity. Backed by a nearly untapped $5B revolving credit facility.
Credit Ratings and Market Sentiment
EOG is the most creditworthy with cash-backed ratings.
COP retains investment-grade despite debt rise; low-cost asset base helps.
MPC’s credit remains intact—but rating agencies are watching leverage closely.
Capital Allocation & Leverage Impact (2024–2025)
Key Takeaways
EOG: Prioritizes dividends, buybacks, and disciplined CapEx—with zero reliance on debt markets.
COP: Balances growth + capital return, but watch for a shift if free cash flow narrows.
MPC: Continues aggressive buybacks but may slow capital returns if debt markets tighten.
Strategic Conclusions: Who’s Winning the Balance Sheet Battle?
Best-in-Class: EOG Resources
Why? Negative net debt, strong liquidity, minimal short-term maturities.
Investor edge: Offers resilience, flexibility, and low dependence on external capital.
Strategic and Stable: ConocoPhillips
Why? Active liability management and diversified cash flows.
Investor edge: Solid core energy exposure with post-M&A leverage under control.
Leveraged Opportunity: Marathon Petroleum
Why? Heaviest debt load, interest-rate sensitivity.
Investor edge: Potential upside if refining margins stay high and rates fall—but higher risk.
Risks to Watch in H2 2025
MPC: Rising interest expense and potential margin compression could force slower buybacks or CapEx.
COP: Execution risk post-MRO deal, especially if oil prices slide.
EOG: Low risk, but watch if they begin a leverage build-up without clear ROI.
Investor Implications: Positioning for 2025 and Beyond
EOG Resources – The Liquidity Fortress:
Best suited for conservative, long-term investors prioritizing downside protection and cash-rich balance sheets. EOG’s negative net debt, disciplined capital structure, and high return-on-capital approach offer resilience in volatile cycles—with steady upside through shareholder returns.
ConocoPhillips – The Strategic Compounder:
An ideal core holding for investors seeking a balanced blend of operational scale, capital returns, and optionality. COP’s proactive debt management, post-acquisition flexibility, and strong investment-grade profile position it well to capitalize on market opportunities while preserving stability.
Marathon Petroleum – The Leverage-for-Yield Play:
Appeals to higher-risk, higher-reward investors willing to embrace debt-driven capital returns and cyclical exposure. MPC’s elevated leverage and dependency on market conditions offer asymmetric upside—if rates ease and refining margins hold, the stock could re-rate. But downside risks are more acute.
This is Financial Insights—where capital structure meets strategy.
Want more deep dives into how oil companies are managing leverage, liquidity, and credit risk?
📩 Subscribe to PetroSymposium and get premium financial commentary, curated for serious energy investors.
References
ConocoPhillips. (2024, December). Senior note issuance press release and debt tender offer announcement. Retrieved from https://www.conocophillips.com/investors
ConocoPhillips. (2024). Q4 and full year 2024 financial results and acquisition impact. Retrieved from https://www.conocophillips.com/investors/financial-reports
EOG Resources. (2024, November). Senior notes issuance and capital allocation update. Retrieved from https://www.eogresources.com/investors
EOG Resources. (2024). Financial statements as of Q3 2024. Retrieved from https://www.eogresources.com/investors/financials
Marathon Petroleum. (2025, February). Senior notes issuance and refinancing activity. Retrieved from https://www.marathonpetroleum.com/investors
Marathon Petroleum. (2025). Q1 2025 financial disclosure and debt profile update. Retrieved from https://www.marathonpetroleum.com/investors/financials
Morningstar DBRS. (2025, March). Credit rating and outlook: ConocoPhillips issuer rating reaffirmation. Retrieved from https://www.morningstardbrs.com
Moody’s Investors Service. (2025, February). Rating action: Marathon Petroleum senior unsecured debt affirmed at Baa2 with stable outlook. Retrieved from https://www.moodys.com
S&P Global Ratings. (2025, February). Marathon Petroleum credit rating report. Retrieved from https://www.spglobal.com/ratings
Fitch Ratings. (2025, February). Marathon Petroleum rating affirmation. Retrieved from https://www.fitchratings.com